

Home - Departments - Wind Resource Assessment (WRA)
The aim of National Institute of Wind Energy under its WRA division is to locate wind rich sites in the country through data analysis for the development of wind energy utilization. The data generated thus from all parts of the country is to be consolidated for the preparation of a National wind resource atlas. Apart from this the division is also involving into wind flow modelling, wind farm layout design, pre-constructional stage energy yield estimation, performance assessment and forecasting related activities using techniques, models and satellite information for the effective exploitation of wind energy. The division is also involved in activities related to the development of offshore wind power projects in the country by supporting in studies and surveys.
In order to identify wind farmable sites in the country, the Government of India launched a national wind resource assessment programme in 1985. The National Wind Resource Assessment Programme was designed for the selection of windy sites, procurement of suitable instruments, design and fabrication of 20 m tall masts, their installation at the selected sites and collection & processing of the data's. Nodal agency of each state also actively participated in the implementation of the programme. After the establishment of the National Institute of Wind Energy (formerly, C-WET) in Chennai, the National Wind Resource Assessment Programme has been transferred to NIWE and the activities of Field Research Unit of Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune (FRU-IITM, Pune) was terminated. Since 2001 the National Wind Resource Assessment Programme is being executed by NIWE on behalf of MNRE. Under the programme, NIWE has commissioned 50m, 80m, 100m and 120m height masts to collect dedicated wind resource data at multi-level.
All the states and the major union territories are covered under this programme. More stations are being added every year so that more uncovered areas in states are studied scientifically. The data collected also serves as data bank for the preparation of national wind potential maps and other research purposes. Under the programme, cumulatively 915 stations have been established as on November 2022. The Ministry is continuing this project through NIWE in association with State Nodal Agencies.
As a part of the programme, in order to provide the authentic knowledge of the wind energy availability in a region of interest to the stakeholders, the Ministry decided to publish the data in a book form. Nine volumes of Wind Energy data books which provide extensive information of the sites where actual wind measurements carried out have been published so far.
As a part of outcome of this study, wind power density maps have been prepared based on the measurements and meso-scale models. In 2005, the wind power potential for 10 states at 50m has been estimated with relevant assumptions. From the discrete values of WPD at individual locations, the wind power potential over an extended area of land have been estimated. In the year 2010, Indian wind atlas was prepared by NIWE with a combined effort from RISO-DTU, Denmark using much sophisticated meso-scale modelling technique called Karlsruhe Atmospheric Meso-scale Model (KAMM). Subsequently, in 2015 NIWE has prepared the Indian Wind potential map 100m AGL (Above Ground Level) and recently the map has been upgraded to 120m AGl to cope up with the increasing hub heights of the wind turbines.
Under take consultancy services on wind resources assessment, micro survey of wind resources, micro sitting and Detailed Project Report (DPR) for wind farm developments.
India is blessed with a coastline of about 7600 km surrounded by water on three sides and has bright prospects of harnessing offshore wind energy. The Government of India notified the National Offshore Wind Energy Policy as per the Gazette notification dated 06 October 2015 to provide a policy framework for the exploitation of offshore wind energy up to the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of the country. Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) is designated as the Nodal Ministry for development of Offshore Wind Energy in India and National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE) is identified as the Nodal Agency for the development of offshore wind energy in the country.
NIWE has carried out preliminary assessment along the Indian coastline through 74 nos. of meteorological mast measurements and through satellite data assessment, which showed reasonable potential along the Gujarat and Tamil Nadu coast. Towards validating the preliminary assessments, NIWE has installed a 100m high guyed lattice mast in the coastal line of Dhanushkodi, Rameshwaram which is a narrow piece of land jutting towards Sri Lanka and surrounded by water in three directions. In order to validate the wind potential at the zones demarcated under FOWIND project, a LiDAR-based offshore wind measurement was initiated by NIWE in Gulf of Khambhat, Gujarat Coast. The two years measurement campaign was successfully completed and structure has also been dismantled.
 |  |  |
| LiDAR measurement campaign at Gulf of Khambhat | ||
NIWE has carried out Geophysical survey at about 365 sq.km (70 sq.km under FOWPI project) in Gulf of Khambhat, Gujarat for the proposed 1 GW offshore wind farm project to ascertain the nature of subsurface and soil profile available at recommended depths for the design of foundation of offshore structures.
Skoch Order-of-Merit was awarded for the project “Wind Power Forecasting by NIWE - Vortex” during the 42nd Skoch summit on 10th- 11th December 2015 at India Habitat Center, New Delhi.
 |
Received National Award for eGovernance 2018-19 (Golden Award under “Outstanding research on citizen centric Services by Academic Research Institutions”) for the project “Wind power forecasting for the whole state of Tamil Nadu” during the ceremony of National Award for eGovernance 2018-19 on 27th February 2019 at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, Janpath, New Delhi.
 |
NIWE established VG forecasting laboratory in year 2017 under the project viz., Centre for Excellence in VG Forecasting with a major objective to create a State of Art Forecasting Laboratory in NIWE for providing wind and solar power forecasting services to Indian Industry.
NIWE has developed In-house Data management system, Indigenous Wind and Solar Power Forecasting model, Monitoring System, Web portal, forecast simulation tools and security system. NIWE is currently providing VG pilot forecasting services and Operation VG forecasting services on commercial basis for various SLDCs.
The accuracy of Wind forecasting for the State of Tamil has hit a milestone of 99% of error blocks within permissible deviation as per CERC norms for both Intra-Day and Day-Ahead forecast in year 2018. NIWE has already signed MoU with Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Karnataka, Andra Pradesh, Maharashtra and Rajasthan SLDC's to establish operation wind power forecasting system. NIWE has proposed to sign MoU with other RE rich states in couple of months.
Error analysis for the whole State of Tamil Nadu is given below,
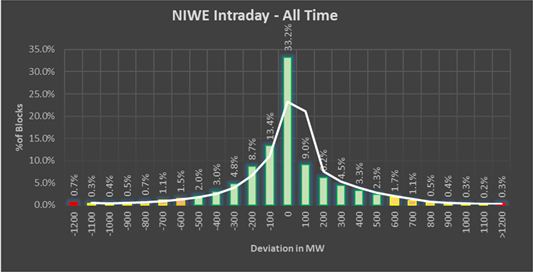 |
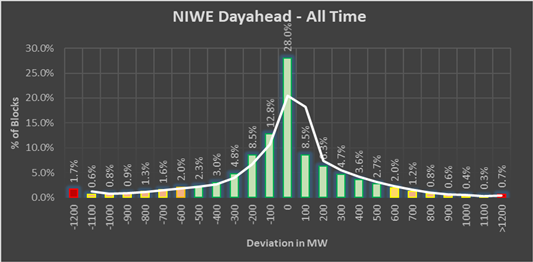 |
Error Analysis for the whole state of Karnataka is given below,
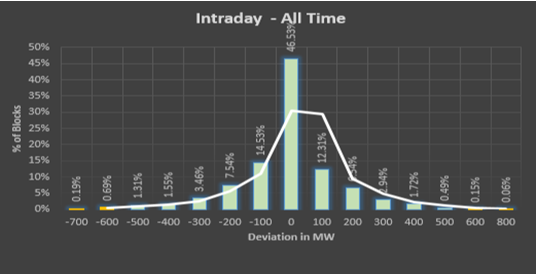 |
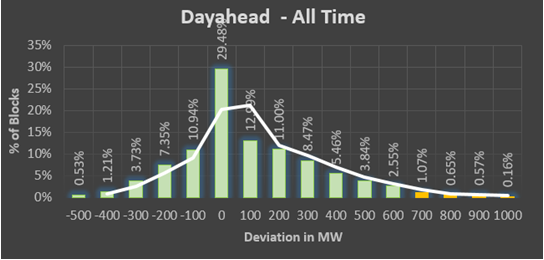 |
Error Analysis for the whole state of Gujarat is given below,
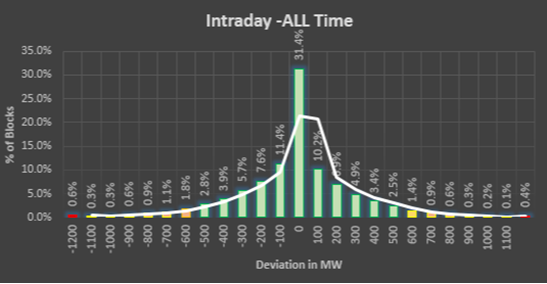 |
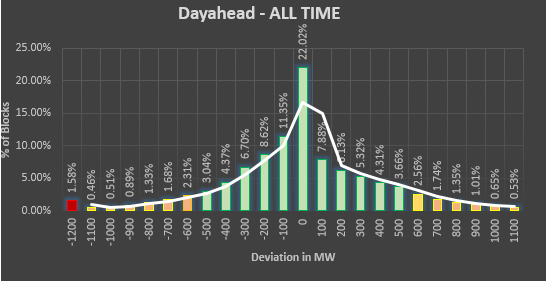 |
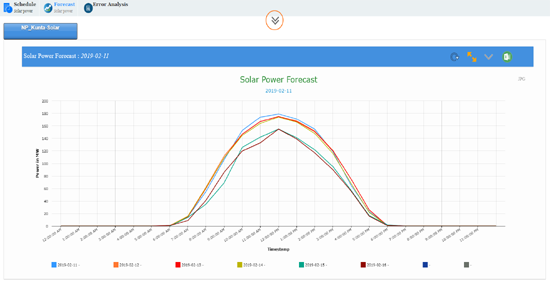
Error Analysis for NP Kunta Solar Park is given below,
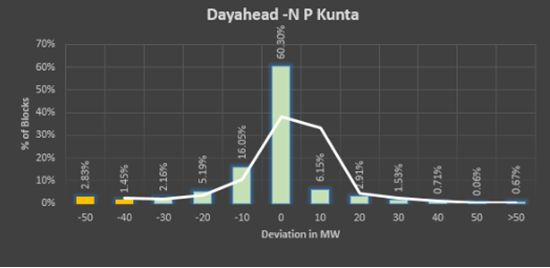 |
Realizing the immense potential and importance of solar energy, Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India launched National Solar Mission (NSM) in 2010 to provide fillip to the promotion of solar industry in the country. This initiative also aims at promoting ecologically sustainable growth to meet the global efforts to mitigate climate changes. The availability of high quality ground measured solar radiation data in the country till 2011 was unreliable and inadequate. Limited sources of data is compiled & published by India Meteorological Department (IMD) stations and satellite data. Non-availability of bankable and investor grade ground measured solar data was a major hurdle in the implementation of solar power projects in the country. To overcome these deficiencies, they launched a national program in 2010 for the establishment of a network of Solar Radiation Resource Assessment (SRRA) stations to collect solar radiation resource data covering GHI, DNI, DHI and associated meteorological parameters in a phased manner through National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE), by establishing an exclusive SRRA unit. Under phase-I program of SRRA, 51 SRRA stations have been commissioned in 10 states and 1 UT and under phase-II sanctioned in 2013. Another 60 SRRA stations have been commissioned in 17 states and 3 UT cover the entire India. Besides the SRRA stations , 4 advanced measurement stations also have been commissioned under phase-II in the country to collect site specific attenuation of solar radiation due to various atmospheric constituents . NIWE has thus established the world's largest solar radiation monitoring network, spread in 115 locations across India. High resolution 1 minute data from these 115 stations are received through GPRS technology in the server established in NIWE and a fully automatic quality control mechanism as per international standard is in force for data cleaning to make the data reliable.
For the development of solar power plants, high quality ground measured solar radiation data is essential.
A typical SRRA station consists of two towers of 1.5 m and 6 m tall. The 1.5 m tall tower is equipped with a solar tracker, one Pyrheliometer and two pyranometers (one with shading disc) to measure direct, global and diffuses irradiance respectively. The 6 m tall tower houses meteorological sensors for measuring ambient temperature, relative humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind speed & direction, rain fall and a state of-the-art data acquisition system. The solar sensors are traceable to World Radiation Centre/World Radiometric Reference (WRC/WRR) and the meteorological sensors are traceable to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) respectively. The SRRA station is powered by solar energy for independent operation and has power autonomy for a week. A trigger switch is also part of the SRRA station to track the cleaning status of the station on a daily basis.
One hundred and eleven (111) SRRA stations have been commissioned in the country in 29 States and 3 Union Territories (UT) during the period May 2011 to June 2014. The specifications of the sensors / instruments used in both the phases are identical, except for the inclusion of lightning arrestor and energy meter in the second phase of SRRA stations. Data collection sampling is 1 sec and basic data average is 1 minute.
Indian Solar Radiation AtlasTo quantify the site specific attenuation of solar radiation due to various atmospheric constituents, four AMS have been established in the country one each in North, East, South and West respectively at National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE),-Gurugram, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology (IIEST)- Howrah, Prathyusha Engineering College (PEC)- Tiruvallur and Gujarat Energy Research and Management Institute (GERMI)- Gandhi Nagar (Gujarat). As the scattering and absorption etc. are wavelength specific, ten independent narrow wavelength channels are used for the solar spectrum analysis. Each wavelength has an independent Collimator and Detector for simultaneous measurement of all wavelengths. AMS is also equipped to provide information on Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) of the atmosphere, reflectivity of the earth's surface (Albedo), incoming long wave radiation (sky radiation) and atmospheric visibility for Research & Developmental purpose.
 |
 |
| Typical SRRA Station | Advanced Measurement Station |
 |
| Calibration Laboratory |
Under this project NIWE proposes to carry out extensive LiDAR based offshore wind resource assessment off the Gujarat coast and Tamil Nadu coasts. In addition to this, NIWE proposes to carry out the Oceanographic / Hydrographic measurements, in and around the LiDAR platforms or suitable locations off the Gujarat coast and Tamil Nadu coast to understand the sea-state conditions, which are envisaged as equally essential and necessary to design the foundation of the Offshore wind turbines, to plan for Installation & other survey activities, and to understand the Weather Window for Operation and Maintenance planning. These simultaneous measurements will help to quantify the wind potential and understand sea-state in a fast-track manner, for effective demarcation of the offshore wind energy blocks.
In Tamil Nadu, three locations at zone B1, Zone C1 & Zone E2 have been identified and the clearance process has been completed.
Reliable background information on the availability of renewable resource and its geographical variation will play a major role in achieving the government's ambitious targets. As the wind speed increases with respect to height, the hub height extension is being looked into one of the effective solutions to enhance the energy yield from the wind turbines. With the technical advancements, the modern day turbines have reached the hub height of 120m to 130m and a further enhancement in hub height is foreseen, which would require higher height maps. Studies have also revealed that solar and winds are almost complementary to each other.
Hybridization of these two technologies would help in minimizing the variability apart from optimally utilizing the infrastructure including land & transmission system and a Hybrid potential map in this regard would be very much helpful for the stakeholders to identify suitable sites for further investigation. NIWE proposes to prepare indicative Renewable Energy potential maps (wind maps at 120m & 150m and Hybrid maps) through advanced numerical meso-scale modeling techniques and validate the maps with Integrated wind and solar masts and remote sensing in-situ ground measurements to move towards achieving the ambitious goals as envisaged by the government.
To cope up with the ever increasing hub height of the wind turbine, NIWE has taken a new initiative to prepare the 120 m wind potential map.
Forecasting Team Capacity, building process was initiated by Over speed, GmbH in collaboration with NIWE in August 2017. Fine tuning of prototype solar power forecasting model is under progress.
 |
 |
 |
Snapshots of forecasting portal:
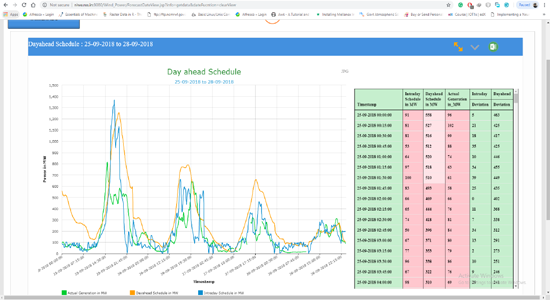 |
| Day ahead Schedule of Wind power Forecasting |
 |
| Week ahead Schedule of Solar power Forecasting |
NIWE has developed state of art in house developed wind/solar power forecasting system to predict wind/solar power upto 7 day-ahead and also provide intraday revisions to support all the State load despatch Centre (SLDC) in the country to evacuate wind /solar power and also to manage grid efficiently.
Variable generation (VG) forecasting service plays an important role in grid management activities of State Load Dispatch Centre (SLDC). In order to utilize the maximum of renewable resources and to increase penetration and evacuation of wind power generation, a demo 51 MW wind power-forecasting project was initiated during 2013 in association with M/s Vortex Spain through an Indo-Spanish research collaboration facilitated by MNRE, Government of India. As a spinoff of the said project, NIWE initiated operational wind power forecasting services to Tamil Nadu since 2015. Subsequently, with the help of Indian NWP data set, an Indigenous wind power-forecasting model was developed by NIWE during 2017. Under Centre for Excellence in VG power forecasting project, NIWE carried out pilot operational wind power forecasting services for the whole state of Gujarat, Karnataka, SRLDC and Maharashtra. NIWE also initiated pilot operational solar power forecasting services to SRLDC. Based on the pilot project experience, NIWE has finetuned its wind and solar power forecasting model. The NIWE forecasting service would assist State -owned electricity generation and distribution utilities for better management of fluctuations in wind power/Solar power output.
MoU signing with various SLDC's for pilot wind/solar power forecasting services
 |
 |
 |
 |
National e-governance Award
 |
IWPA Review Meeting
 |
Celebration of Cyber Jaagrookta Diwas (CJD) on 6th Oct 2022
 |
Developed an Indigenous solar power forecasting model for the country with the technical support of GIZ, New Delhi in 2019.
A concept feasibility study on Virtual Power Plant (VPP) in India in association with GIZ GmbH, New Delhi, Fraunhofer IWES, Germany and ICF International has been initiated. Virtual Power Plant is a network of decentralized, medium-scale power generating units such as, wind farms, biomass and solar parks as well as flexible power consumers and batteries. The sources are often a cluster of distributed generation systems, and are often orchestrated by a central authority
 |
 |
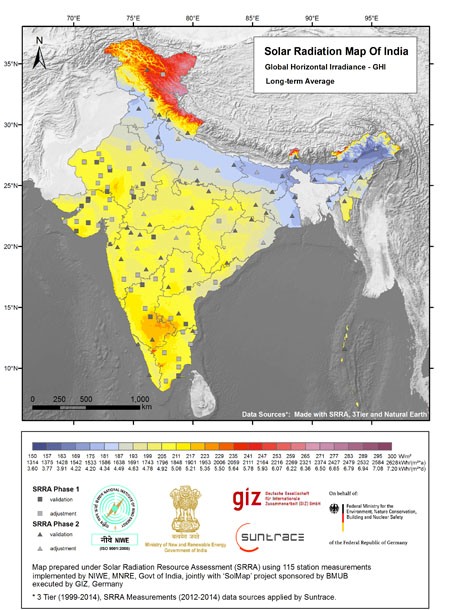 |
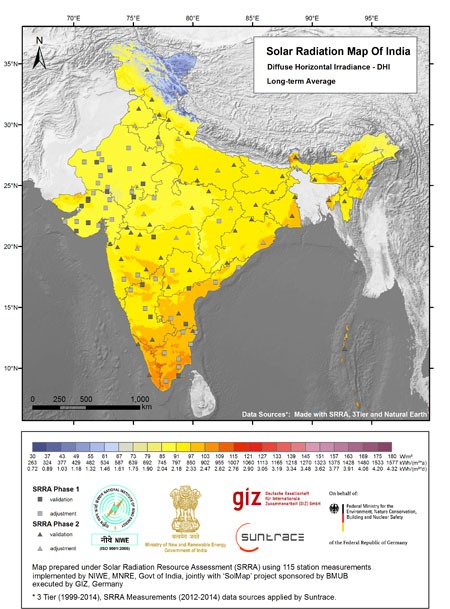
| Atlas DHI | Atlas DNI | Atlas GHI |